
WELCOME TO THE FIFTH GRADE!!!!
UNIT 6: ELECTRICITY
Objectives
- The important role electricity plays in our daily lives.
- The particles that make up an atom and the role they play in attaction and repulsion.
- The difference between static and current electricity and their applications.
- Electrical circuits.
- Famous inventors and inventions.
Types of ELECTRICITY
Electrical charge
Electrical circuits
What Causes Thunder and Lightning?
Lightning is a powerful burst of electricity that happens very quickly during a thunderstorm.
Lightning is caused by an electrical charge in the atmosphere that is unbalanced.
The movement of rain and ice inside a thundercloud creates an electrical charge, with the negative charge (electrons) forming at the bottom of the cloud and the positive charge (protons) forming at the top.
Opposites attract so the negative charge at the bottom of the cloud seeks out a positive charge to connect with.
Lightning can occur inside clouds, between clouds and from clouds to the ground.
Around one quarter of lightning is from cloud to ground.
When lightning strikes the ground it seeks out the shortest route to something with a positive charge, this might be a tree, a tall building or if they’re very unlucky, a person.
UNIT 5: SOUND, LIGHT AND HEAT
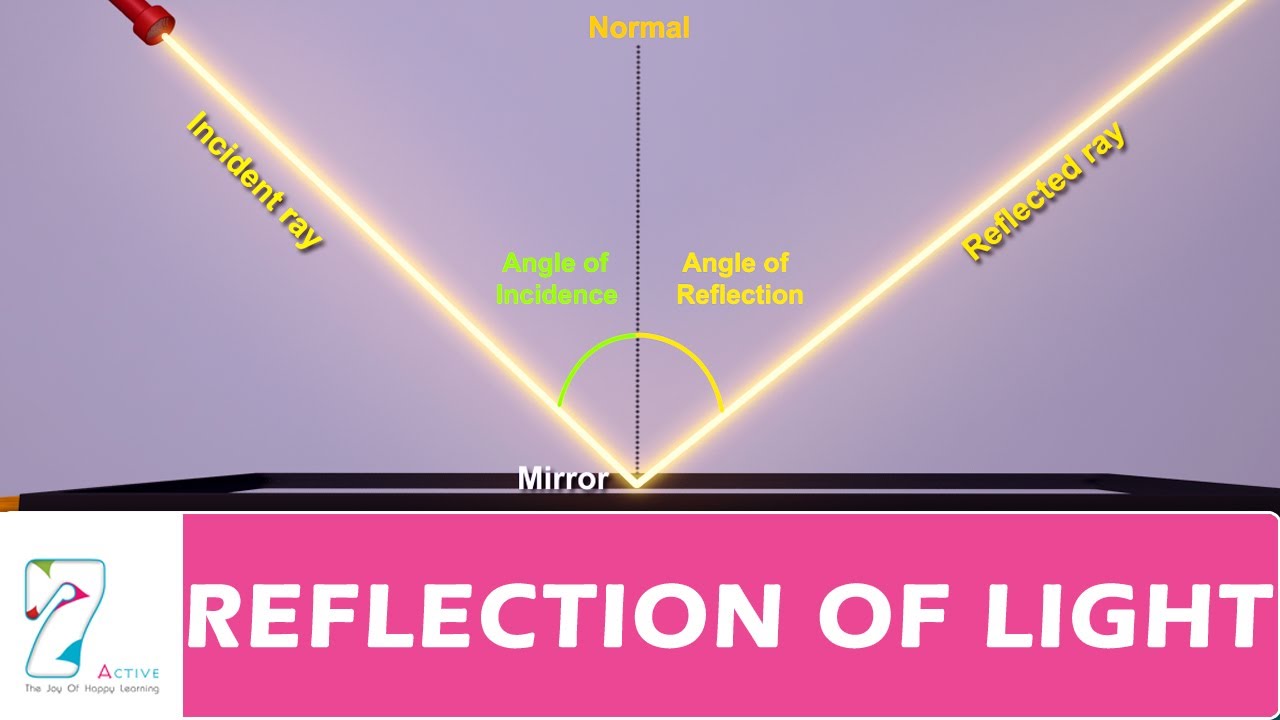
SOUND
Sound comes from vibrations. These vibrations create sound waves (NOT STRAIGHT LINES) which move through mediums such as air and water before reaching our ears.
States of matter related to heat
UNIT 4: ENERGY
Different forms of energy
The Difference Between Kinetic and Potential Energy
AIR POLLUTION
https://climatekids.nasa.gov/trivia/
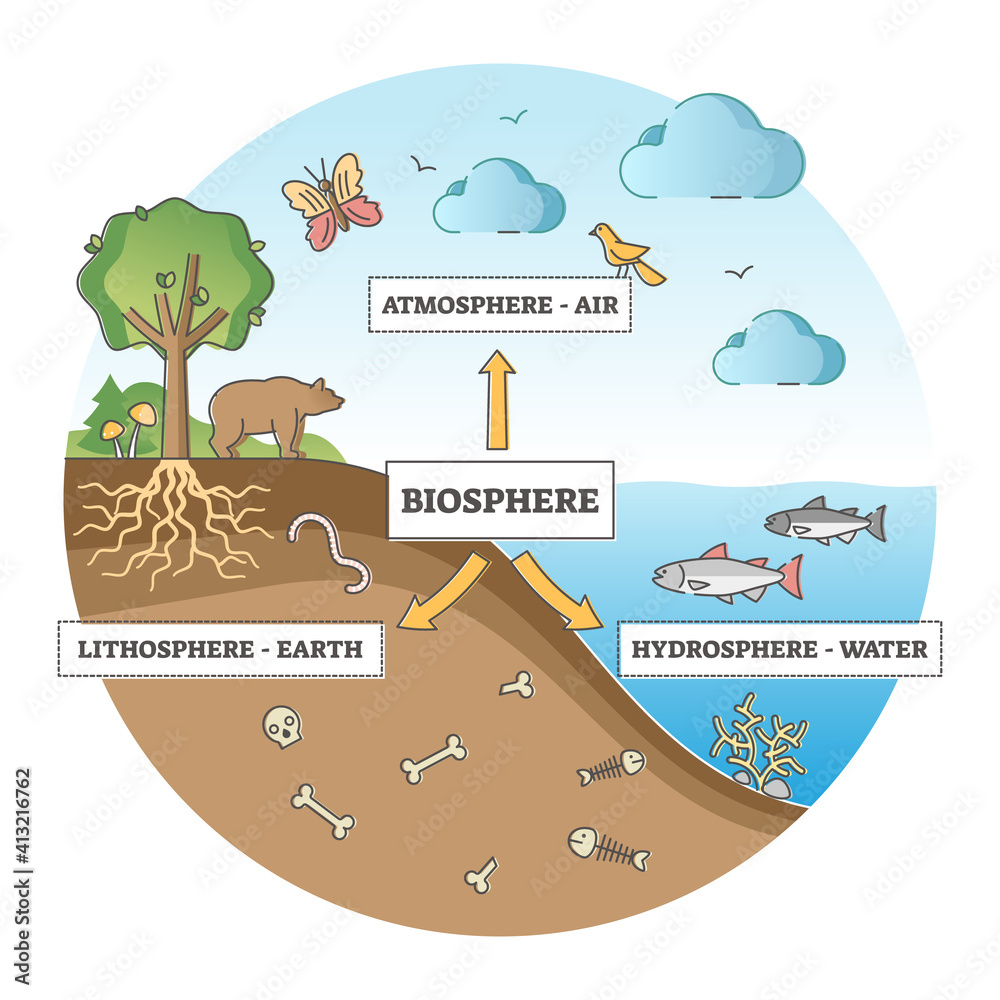
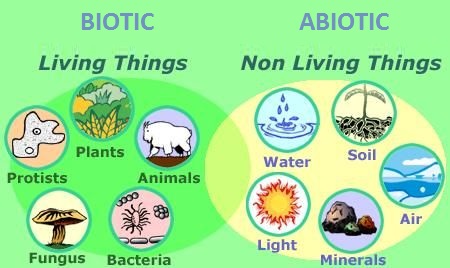
UNIT 2: ECOSYSTEMS
1. The principle characteristics and components of an ecosystem.2. How populations, communities and ecosystems are structured.3. How organisms adapt to their habitat.Coniferous VS Deciduous Trees
UNIT 1. LIVING THINGS
All living things are made up of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. (Todos los seres vivos están formados por células. Las células son la unidad básica de vida).
*Plant and animal cells are different shapes and have different components, but most cells have a nucleus, a membrane, cytoplasm and organelles. (Las células vegetales y animales son de diferentes formas y tienen diferentes componentes , pero la mayoría de las células tienen núcleo ,membrana, citoplasma y orgánulos).
*Unicellular organisms are made up of only one cell. (Los organismos unicelulares están hechos de una sola célula).
*In multicellular organisms, such as animals, groups of cells work together to carry out a variety of functions. Each type of cell has a specifc function within the organism. (En los organismos pluricelulares, como los animales, diferentes grupos de células trabajan juntos para llevar a cabo una gran variedad de funciones.Cada tipo de célula tiene una función específica en el organismo).
*The cells are different shapes according to their function. (Las células tienen diferentes formas según su función).
*Cells join together to form tissue. Organs are made up of different tissues. Systems are groups of organs that work together to perform a function. (Las células se unen para formar un tejido. Los órganos están formados por diferentes tejidos. Los sistemas son grupos de órganos que trabajan juntos para llevar a cabo una función).
*The basic life processes are carried out by different systems. (Los procesos vitales son llevados a cabo por diferentes sistemas).
*Plants are organised in a similar way to animals and other multicellular organisms. They have cells, tissues, organs and systems. Most plants have three main parts: a stem, roots and leaves. (Las plantas están organizadas de manera similar a los animales y otros organismos pluricelulares.Tienen células,tejidos,órganos y sistemas.La mayorís de las plantas tienen tres partes: tallo,raíces y hojas).
*All living things carry out the basic life processes of interaction, nutrition and reproduction, but they do this in different ways. (Todos los seres vivos llevan a cabo las funciones vitales: relación, nutrición y reproducción, pero lo hacen de manera diferente).
*All living things take in essential nutrients from their environment. (Todos los seres vivos toman nutrientes de su entorno).
*These nutrients give them energy and enable them to grow and develop. (Estos nutrientes aportan energía y permite que crezcan y se desarrollen).
*Animals have different types of reproduction. They use their reproductive systems to make new individuals. (Los animales tienen diferentes tipos de reproducción.Utilizan un sistema reproductor para crear nuevos individuos).
*Like other living things, plants interact with their environment. Like all other living things, plants reproduce to make new individuals. They can reproduce in different ways. (Como otros seres vivos las plantas interaccionan con el medio. Como todos los seres vivos las plantas se reproducen para crear nuevos individuos. Pueden reproducirse de diferentes maneras).
"The Plant Cell Clique"
THE CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
We classify living things into groups called kingdoms. There are five different kingdoms: the Monera, Protoctista, Fungi, Plant and Animal kingdoms. (Podemos clasificar los seres vivos en grupos llamados reinos. Hay cinco reinos diferentes: Monera, Protoctista, Fungi, Plantas y Animal).
* Bacteria belong to the Monera Kingdom. Monerans are microscopic, but not all share the same characteristics. (Las bacterias pertenecen al reino Monera. Son microscópicas, pero no todas comparten las mismas características).
* Algae and protozoa belong to Protista kingdom. There is a wide variety of protoctists. Each type has specific characteristics (Las algas y los protozoos pertenecen al reino Protoctista. Hay una amplia variedad de protoctistas. Cada especie tiene características específicas).
* Mushrooms, mould and yeast are all fungi. They have several characteristics in common. (Las setas, el moho y la levadura son hongos. Tienen algunas características en común).
* Plants form part of the Plant Kingdom. As members of the same kingdom, all plants have some characteristics in common. For example, they have cells with a rigid cell wall and they perform photosynthesis. (Las plantas forman parte del reino Plantas. Como miembros del mismo grupo, todas las plantas tienen algunas características en común. Por ejemplo, sus células tienen una pared celular rígida y pueden llevar a cabo la fotosíntesis).
*Seed plants reproduce by creating seeds. There are two main types of seed plant: angiosperms and gymnosperms. (Las plantas con semillas se reproducen mediante semillas. Hay dos tipos principales de plantas con semillas: las angiospermas y las gimnospermas).
* Angiosperms grow flowers. That is why they are also called flowering plants. Fruit grows from the pollinated flowers and the seeds grow inside the fruit. (Las plantas angiospermas producen flores. Por eso se pueden conocer también como plantas florecientes. Los frutos crecen a partir de las flores fertilizadas y las semillas crecen dentro de los frutos).
* Gymnosperms produce cones. The largest group is called conifers. The seeds grow inside the cones. Some conifer seeds are called nuts. (Las plantas gimnospermas producen conos. El grupo más grande se llama coníferas. Las semillas crecen dentro de los conos. Algunas semillas se llaman piñones).
* Non-seed plants, such as ferns and mosses, don’t have seeds. They produce special cells called spores. When spores fall to the ground, they grow into new plants. (Algunas plantas sin semillas, como los helechos y los musgos, no producen semillas. Generan unas células especiales llamadas esporas. Cuando las esporas caen al suelo, crecen dando lugar a una planta nueva).
* Invertebrates are animals that don’t have a backbone. They belong to the Animal Kingdom. Invertebrate animals are classified into six groups: porifera, cnidarians, annelids, molluscs, arthropods and echinoderms. (Los invertebrados son animales que no tienen espina dorsal. Pertenecen al reino Animal. Se clasifican en seis grupos: poríferos, cnidarios, anélidos, moluscos, artrópodos y equinodermos).
* Vertebrates form part of the Animal Kingdom. They are multicellular animals that have a backbone. They are classified into five groups: mammals, reptiles, fish, birds and amphibians. (Los vertebrados forman parte del reino Animal. Son animals pluricelulares que tienen espina dorsal. Son clasificados en cinco grupos: mamíferos, reptiles, peces, aves y anfibios).
Classification of Living things
UNIT 6: ELECTRICITY
Objectives
By the end of this unit, you will have achieved a greater understanding of the following concepts:
the important role electricity plays in our daily lives
the particles that make up an atom and the role they play in attraction and repulsion
the difference between static and current electricity and their applications
famous inventors and inventions.
What is a food chain?
All living things needs food to survive.
A food chain shows how each living thing gets food, and how nutrients and energy passes on from creature to creature, or from environment to creature. Below is a basic example of a food chain.
A food web
Many FOOD CHAINS make up a FOOD WEB.
Below is an example of a food web:
See how many different food chains can make up a food web?
- This video will show you the difference between food chains and food webs.

How oil harms marine environments
Oil Spill Facts: Lesson for Kids👇
Prestige sinking, one of the worst oil spills in Europe.
UNIT 2: ECOSYSTEMS
Throughout this unit we will learn the following concepts:1. The principle characteristics and components of an ecosystem.2. How populations, communities and ecosystems are structured.3. How organisms adapt to their habitat.What Makes Up The Ecosystem?
SAVANNAH
Coniferous VS Deciduous Trees
Types of Trees Song
UNIT 1: Living things
The 5 kingdoms of living thingsWatch this video, please.
THE CELL
Animal and plant cells are different:

The plant cell and its parts
Cells, Tissues, and Organs
Like all living organisms, the human body is made up of cells. There are all different types of cells in the human body. When lots of similar cells work together to perform a function, they
make up tissue. There are four main types of tissue in the human body including muscle tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue, and nervous tissue.
Organs are somewhat independent parts of the body that carry out special functions.
They are made up of tissues. Examples of organs include the eyes, heart,
lungs, liver, and stomach.
Cell Tissue Organ System Organism
Viro the virus

What is Coronavirus? An explainer for Children.
Tuesday 19th May

Top 10 Inventions of All Time




Simple Machines - Archimedes Screw.
Do not do it, just watch the video!!!
15 Accidental Inventions You Can't Imagine Your Life Without


The Simple Machine Song
Simple Machines
Simple and Complex Machines

Have a good weekend!!😉😘




Sink or Float?
Friday 24th April



Magnets and Magnetism
Thursday 23rd April



Gravity, Force and Work
Wednesday 22nd April
A Force is a Push or Pull
Forces That Cause Change
Tuesday 21st April
Monday 20th April
Friday 17th April

Thursday 16th April
Extra information!!!
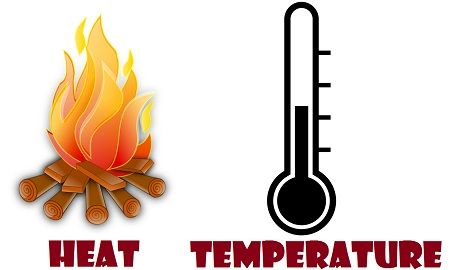
When we add thermal energy to a subtance, the state of the substance changes or the volumne of the substance increases.
👇You can write a comment below! 😉
Wednesday 15th April 2020
Pupil’s book page 56
🎈
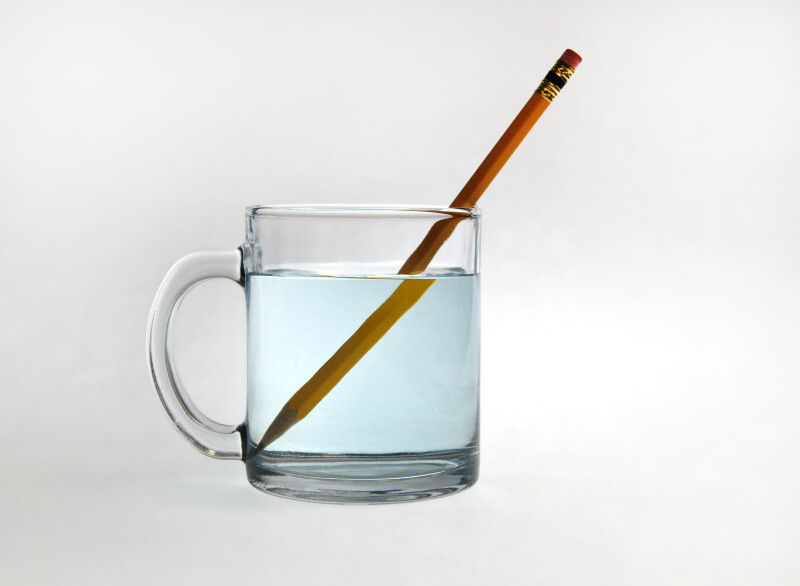
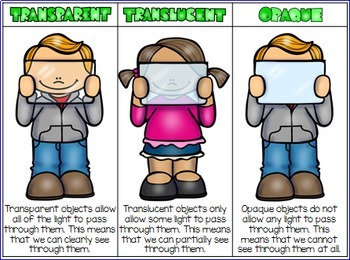
What is matter?



Unit 5: Which forces are invisible?
- English Castellano
- Atom átomo
- attract atraer
- buoyancy flotabilidad
- condense condensar
- conductor conductor
- density densidad
- elastic elástico
- evaporate evaporar
- friction fricción
- gram gramo
- gravity gravedad
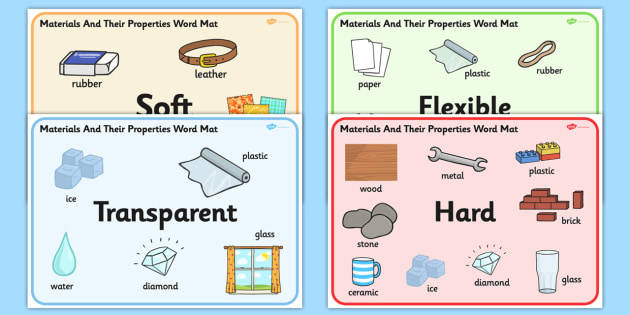
- hard duro
- hardness dureza
- inelastic inelástico
- insoluble insoluble
- insulator aislante
- kilogram kilogramo
- magnetism magnetismo
- mass masa
- matter materia
- melt derretir
- mould moldear
- occupy ocupar
- property propiedad
- repel repeler
- rubber goma
- solidify solidificarse
- soluble soluble
- volume volumen






































































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario